Payroll refers to the process of compensating employees for their work, including calculating and paying salaries, wages, bonuses, and deductions. The payroll process typically involves determining the hours worked by employees, calculating the correct amount of pay based on their hourly rate or salary, withholding taxes and other deductions, and issuing payments to employees either through direct deposit or physical checks. The payroll process is important for both employees and employers as it affects an employee’s take-home pay and is used to calculate various tax liabilities for the company.
Types of Payroll

There are several types of payroll systems, including:
Manual Payroll:
Manual payroll refers to a system of calculating and distributing employee salaries and wages without the use of automated payroll software. In a manual payroll system, the employer or designated payroll administrator is responsible for calculating each employee’s pay, taking into account hours worked, overtime, deductions, and any other pay components. This involves manually calculating and recording each employee’s pay and deductions, typically using a spreadsheet or paper-based system.
Automated Payroll:
Automated payroll refers to a system for calculating and distributing employee salaries and wages using computer software. Automated payroll systems automate many of the manual tasks involved in the payroll process, such as calculating pay, determining deductions, and issuing paychecks. This uses software or an online platform to automate the calculation and recording of employee pay and deductions.
Outsourced Payroll
Outsourced payroll refers to the practice of hiring an external company to manage an organization’s payroll responsibilities. This can include tasks such as calculating employee pay, tracking hours worked, determining deductions, issuing paychecks, and reporting payroll taxes to the government. This involves hiring a third-party payroll service provider to handle the payroll process on behalf of the company
In-House Payroll:
In-house payroll refers to the practice of managing an organization’s payroll responsibilities internally, using its own staff and resources. This typically involves tasks such as calculating employee pay, tracking hours worked, determining deductions, issuing paychecks, and reporting payroll taxes to the governmentThis involves managing the payroll process within the company, typically using automated payroll software.
Integrated Payroll:
This involves integrating payroll with other HR functions, such as time and attendance tracking, benefits administration, and tax compliance.
Each type of payroll system has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of payroll system will depend on the size and needs of the company, as well as budget and resource constraints.
Advantages of Payroll Services
Accuracy: Payroll services use sophisticated software and expert knowledge to ensure that payroll calculations are accurate and compliant with tax laws and regulations.
Time-saving: Payroll services automate many of the manual tasks involved in the payroll process, freeing up time for HR and finance staff to focus on other tasks.
Cost-effective: For small businesses, outsourcing payroll to a payroll service can be more cost-effective than hiring an in-house payroll specialist or investing in software and infrastructure.
Compliance: Payroll services stay up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations, helping to ensure that the company remains compliant and avoids costly penalties.
Peace of mind: Outsourcing payroll to a payroll service provider gives business owners and HR staff peace of mind knowing that their payroll is being handled by professionals.
Disadvantages of Payroll Services
Cost: Although outsourcing payroll can be cost-effective for small businesses, it can become more expensive for larger organizations.
Lack of control: Outsourcing payroll means that the company has less control over the payroll process and may need to rely on the payroll service provider for important decisions and updates.
Data security: When outsourcing payroll, the company needs to be confident that their sensitive employee data is being handled securely by the payroll service provider.
Limited customization: Payroll services may have limited customization options, making it difficult for the company to tailor the payroll process to their specific needs.
Dependence on technology: Automated payroll services rely on technology, which can be prone to errors or outages. This can result in payroll processing delays or incorrect payments to employees.
Cost: Although outsourcing payroll can be cost-effective for small businesses, it can become more expensive for larger organizations.
Lack of control: Outsourcing payroll means that the company has less control over the payroll process and may need to rely on the payroll service provider for important decisions and updates.
Data security: When outsourcing payroll, the company needs to be confident that their sensitive employee data is being handled securely by the payroll service provider.
Limited customization: Payroll services may have limited customization options, making it difficult for the company to tailor the payroll process to their specific needs.
Dependence on technology: Automated payroll services rely on technology, which can be prone to errors or outages. This can result in payroll processing delays or incorrect payments to employees.
Payroll software programs
There are many payroll software programs available on the market, each with its unique features and capabilities. Here are some of the most popular payroll software programs:
ADP: ADP is a well-established payroll software program that offers a range of solutions for businesses of all sizes, from small businesses to large corporations.
QuickBooks: QuickBooks is a popular accounting software program that includes payroll functionality. It is designed for small to medium-sized businesses.
Xero: Xero is all-in-one accounting software that includes payroll functionality. It is designed for small businesses and has a user-friendly interface.
Gusto: Gusto is a cloud-based payroll software program that offers a range of features, including direct deposit, tax compliance, and employee self-service portals.
Sage 50cloud Payroll: Sage 50cloud Payroll is a payroll software program designed for small to medium-sized businesses. It includes features such as direct deposit, tax compliance, and time and attendance tracking.
Workday: Workday is a cloud-based human resources and payroll software program designed for large corporations. It offers a range of features, including payroll processing, time and attendance tracking, and benefits administration.
Paychex: Paychex is a payroll software program that offers a range of solutions for small to mid-sized businesses, including payroll processing, tax compliance, and direct deposit.
These are just a few examples of the payroll software programs available on the market. The choice of software will depend on the size and needs of the company, as well as budget and resource constraints. It is important to carefully evaluate the features and capabilities of each software program to ensure that it meets the company’s needs.
How to Calculate Payroll Taxes
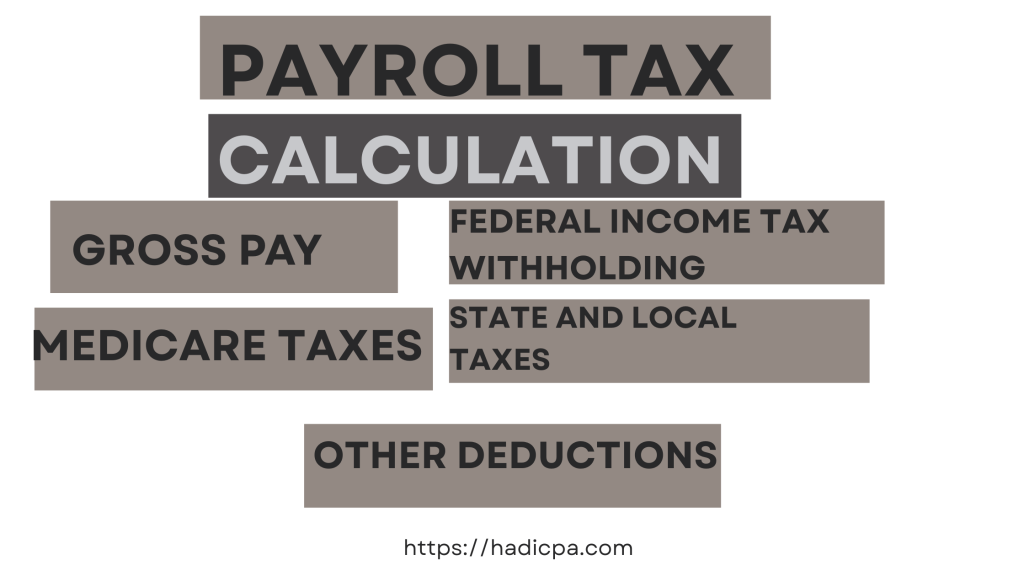
Calculating payroll taxes involves determining the amount of money to be withheld from an employee’s pay for various federal, state, and local taxes. The process typically involves the following steps:
Determine gross pay: Calculate the employee’s gross pay, which is the total amount earned before any taxes or deductions are taken out.
Determine federal income tax withholding: Use the employee’s W-4 form and the IRS withholding tables to determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from their pay.
Determine Social Security and Medicare taxes: The Social Security tax rate is 6.2% of the employee’s gross pay, up to a maximum taxable amount. The Medicare tax rate is 1.45% of the employee’s gross pay, with no maximum taxable amount.
Determine state and local taxes: Check the laws in your state and local jurisdiction to determine if there are any state or local taxes to be withheld, such as state income tax or local taxes.
Determine other deductions: Determine if the employee has any other deductions, such as 401(k) contributions, insurance premiums, or wage garnishments.
Subtract taxes and deductions: Subtract the total amount of taxes and deductions from the employee’s gross pay to determine the net pay, which is the amount of money the employee will receive in their paycheck.
It is important to note that payroll tax laws and regulations are subject to change, so it is important to stay informed of any updates and to consult a payroll professional if you have questions about calculating payroll taxes.
Is Payroll Part of HR or Accounting?
Payroll can be considered a function of both the Human Resources (HR) and Accounting departments, depending on the organization’s structure and size.
In larger organizations, payroll is typically handled by a dedicated payroll department, which may fall under the HR department or the Accounting department. In smaller organizations, payroll responsibilities may be divided between HR and Accounting or handled by a single individual who performs both HR and accounting functions.
Regardless of where it falls organizationally, payroll involves both HR and accounting processes. HR is responsible for maintaining accurate records of employee information and hours worked, while accounting is responsible for ensuring that payroll taxes and other deductions are accurately calculated and processed. The two departments work together to ensure that employees are paid accurately and on time.
What Distinguishes Salary from Payroll?
Payroll and salary are related but distinct terms.
Payroll refers to the total amount of money a company pays to its employees in a given period, typically a month or a year. It includes the salaries of all employees, as well as any bonuses, commissions, or other forms of compensation.
Salary, on the other hand, refers to a specific form of compensation that is paid to employees regularly, usually on a weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly basis. A salary is typically expressed as a fixed amount of money, regardless of the number of hours worked. For example, an employee with a salary of $50,000 per year would receive a fixed amount each pay period, regardless of whether they worked 40 hours or 60 hours in that period.
So, in summary, payroll refers to the total amount of money a company pays to its employees, while salary refers to a specific form of compensation that is paid to employees regularly.
conclusion
Payroll processing is a difficult, time-consuming task that needs to follow stringent federal and state laws and regulations. It demands proper recording and focuses on the small print. Cloud-based software is frequently used by small firms to manage payroll. Other businesses opt to outsource their payroll operations or spend money on an integrated Application system that controls both accounting and payroll.
If you need any assistance please feel free to contact us or follow our Facebook page.





